The heart can occasionally get affected during COVID infection. This is reported in patients with prior heart disease and without heart disease. The heart may be affected due to stress associated with the infection, low oxygen levels in the blood, build-up of toxins in the blood, or damage to coronary arteries that supply the heart. The heart is affected in up to 7 to 28 percent of cases of Covid-19 infection.
STRESS CARDIOMYOPATHY IN COVID 19
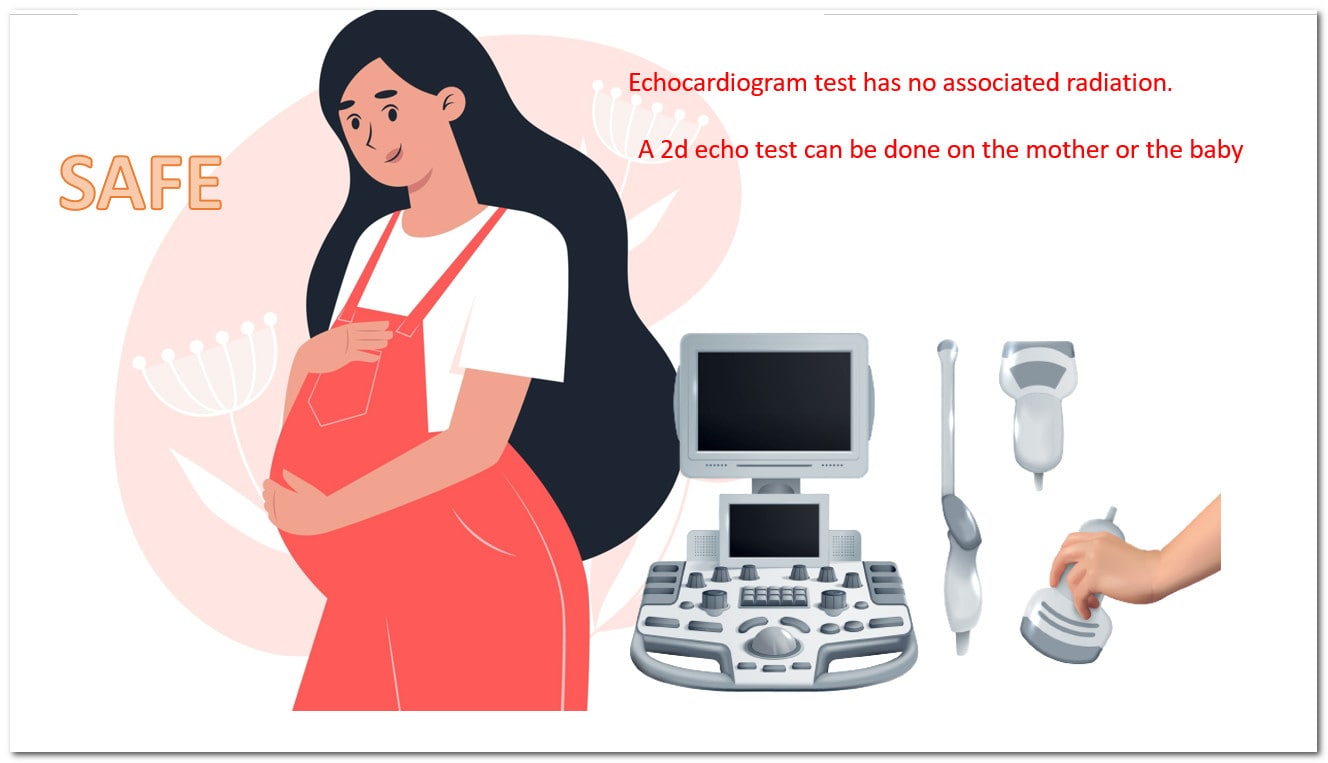
Extreme emotional or physical stress sometimes may lead to sudden enlargement of the heart, called stress cardiomyopathy. It is often a temporary problem and reverses to a normal heart after a few days. 2d echo test plays a crucial role in establishing the diagnosis of stress cardiomyopathy. Covid-19 infection is causing patients to feel anxious, distressed, or worried. Disturbed mental health sometimes elevates adrenaline hormones enormously in the body, making the patient prone to stress cardiomyopathy. Stress cardiomyopathy can sometimes lead to sudden death and heart failure. These patients may develop dangerous arrhythmias also. There is no specific treatment for stress cardiomyopathy, but supportive therapy often manages it.
Symptoms of stress cardiomyopathy are
- Sudden onset of chest pain
- Shortness of breath or Dyspnoea
- Palpitations – faster heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or giddiness
Tests for stress cardiomyopathy
- ECG
- 2d echo test
- Troponin
Treatment for stress cardiomyopathy
- Supportive treatment
Myocarditis by Corona Virus
Inflammation and heart muscle damage caused by Covid-19 infection is known as myocarditis. The damaged heart muscle may not pump the blood effectively, which leads to heart failure. Heart failure may lead to the building up of fluid in the body, which manifests as lung congestion, ankle swelling, and abdominal swelling. The damaged heart muscle may beat rapidly or irregularly, called arrhythmia. Even the Covid-19 vaccine is attributed to some cases of myocarditis.
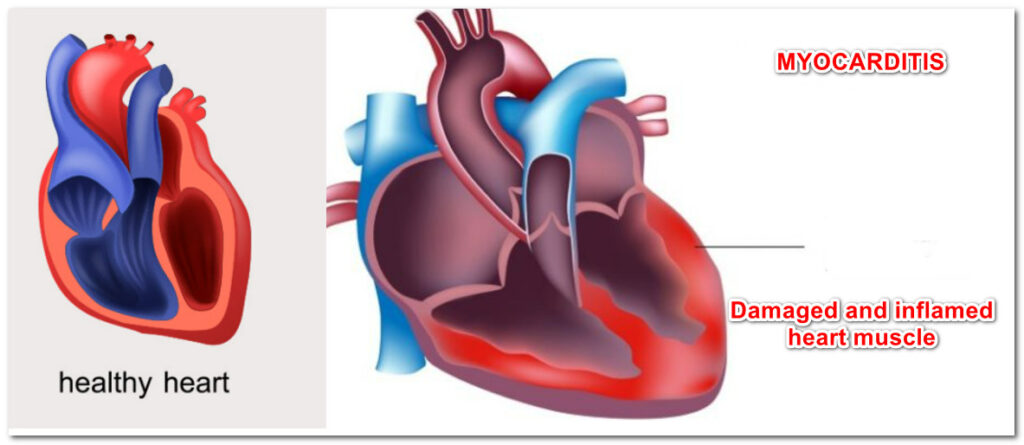
Symptoms of myocarditis
- Chest pain
- Pounding heart/ Thumping in the chest/palpitations
- Shortness of breath, at rest or during minimal physical activity
- Fluid buildup with ankles swelling (Swollen legs), tummy selling (stomach swelling)
- Fatigue
Tests for myocarditis
- ECG
- 2d echo test
- Troponin
- Biopsy
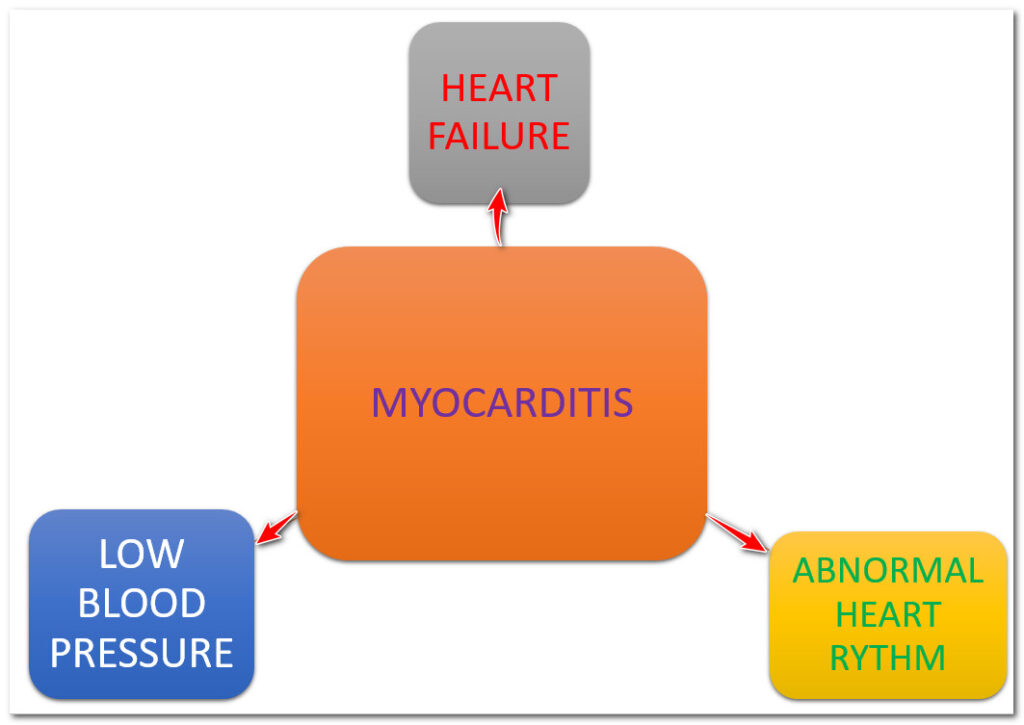
Treatment of myocarditis
Again, there is no specific treatment to covid 19-related myocarditis. Treatment mainly comprises supportive therapy.
ARRHYTHMIAS RISK WITH CORONAVIRUS
Covid-19 infection can cause abnormal heart rhythm. This can cause either too fast or a slow heartbeat—low blood oxygen due to lung involvement in Covid-19 infection-prone the heart for abnormal heart rhythm. Hormones released by the body against Covid-19 can predispose the heart to more arrhythmias. Myocarditis and heart attack (myocardial infarction) can cause abnormal heart rhythm. Medications that are given during hospital stay also increase the risk of arrhythmias. Abnormalities in blood potassium and calcium, which can sometimes be seen during Covid-19 infection, can cause abnormal heart rhythm.
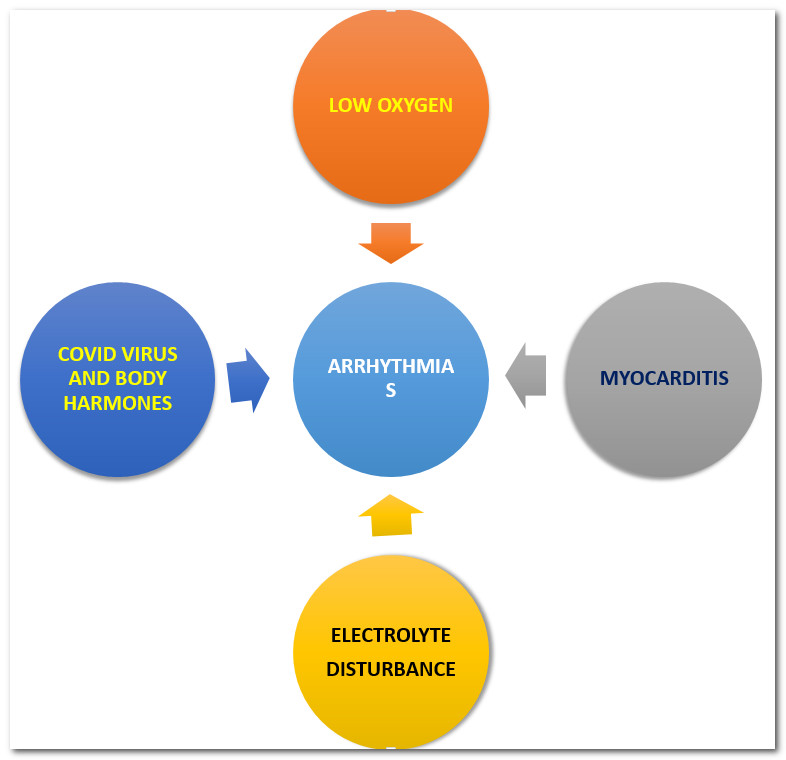
ECG and Holter tests are needed to establish the diagnosis of arrhythmia. Treatment depends on the type of arrhythmia and the patient’s clinical condition.
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) in Covid-19
Covid 19 infection can rarely halt the heart function, which leads to sudden, unexpected death. The person during cardiac arrest collapse and loses consciousness suddenly. It carries a poor prognosis and needs prompt CPR.
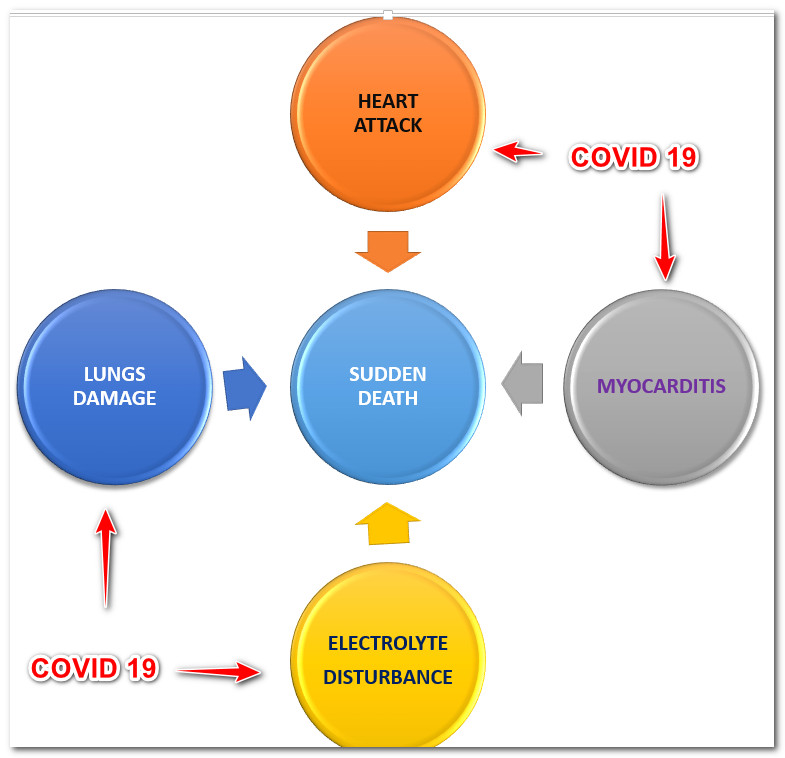
Heart attack in Covid-19
COVID-19 infection is linked to an increased risk of a heart attack. This Heart attack risk is more for patients already suffering from heart diseases, diabetics, and high blood pressure and who are elderly. COVID-19 can cause a person’s blood to thicken, and blood gets clotted very quickly. These clots can be formed in the lungs, brain, kidney, and heart. Therefore these people are more prone to heart attack and brain stroke. This risk stays not just during Covid-19 infection but even up to 4 to 8 weeks after that. A patient cured of Covid-19 illness can get a massive heart attack within one month. Even mental stress due to Covid-19 infection increases the risk of heart attack; sometimes, the Covid-19 virus damages the coronary arteries that supply the heart and causes a heart attack. Sometimes hormones released by the body in response to the Covid-19 virus may damage the coronary artery and make it more prone to a heart attack.
Symptoms of a heart attack may get masked or altered in the presence of covid-19 infection, which makes the diagnosis difficult. This leads to delayed treatment and poor outcomes. Patients with heart attacks visit the hospital later due to fear of exposure to COVID-19, which again delays the treatment. A patient with a heart attack due to covid-19 infection who is on ventilatory support can not report symptoms of a heart attack. In such a condition, a heart attack has to be diagnosed with the help of an ECG test and troponin test.
Most patients with heart attacks due to Covid-19 can be managed with medicine without performing stenting surgery. Urgent or emergent treatment for heart attack by angioplasty or stent surgery is done even when the patient is having Covid-19 if doing so improves the patient condition. Testing for COVID-19 is not possible during a heart attack as it is a medical emergency, and one could not wait till the report comes. Sometimes, the patient is so critically ill due to COVID-19 infection due to severely damaged lungs that doing stenting surgery is not justifiable and also carries a high risk. If the patient is not sick critically, stenting surgery can be done even when the patient has Covid-19. Use of personal protective equipment for all staff in the operation theatre or Cath-lab is mandatory in such cases.
Myocarditis caused by covid 19 infection can mimic a heart attack for which doing stenting surgery, or angioplasty is not helpful. Myocarditis may produce similar symptoms and ECG changes as a heart attack and confuse the treating doctor. Myocarditis should be carefully excluded before taking the patient for angioplasty. If myocarditis seems more likely than heart attack, medications for heart attack can be started without taking the patient for angioplasty until the diagnosis becomes clearer.
Fibrinolytic therapy is sometimes an alternative to angioplasty in particular heart attack patients. An injection is given capable of lysing the clot in the coronary arteries that reestablishes blood flow to the heart muscle. It is associated with less risk of contracting Covid-19 infection in the hospital staff. Few hospitals with fewer resources may utilize this option for most patients with heart attacks.
If stenting surgery or angioplasty has to be done electively, it is recommended to delay it, and this approach will protect the patient and hospital staff from Covid-19 exposure. When patients need bypass surgery, performing stenting surgery is recommended as it is associated with less risk of Covid-19 exposure. Angioplasty is associated with less hospital say and hence less risk for Covid-19 exposure.
All medications used for heart attacks, such as aspirin, heparin, and statin, can be safely given even in the covid 19 patient.
Heart-related mortality in COVID-19 patients
In patients with heart attack and concomitant COVID-19, the risk of death is higher when compared with patients with a heart attack who do not have COVID-19.
Patients with underlying high blood pressure and diabetes will have higher death rates than patients without these comorbidities.
The higher the troponin levels in the blood, the worse the prognosis, Every hospital is now measuring blood troponin levels in every patient admitted with covid 19. ECG has become mandatory for every patient with covid 19, even without chest pain.
Electrocardiogram and COVID-19
All patients in whom COVID-19 is suspected should have a baseline ECG performed when entry into the hospital. Ecg can be abnormal in covid due to multiple reasons.
Troponin levels and COVID-19
Blood troponin levels are elevated in about 10 to 30 percent of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Most patients with troponin elevation and COVID-19 will not have a heart attack, and it is predominantly due to non-specific elevation or myocarditis. Hospitals obtain a troponin soon after admission in all patients.









Pingback: Bradycardia or slow heart rate - DM HEART CARE CLINIC